Ansible role: virt_install_vm 1.0.0 released
I wrote a few articles:
- Howto use centos cloud images with cloud-init on KVM/libvirtd
- Howto use cloud images on the Raspberry PI 4
on my blog on how to use cloud images with cloud-init on a “non-cloud” environment.
I finally took the time to create an Ansible role for it. You’ll find the READE.md below.
Virt_install_vm 1.0.0 is available at: https://github.com/stafwag/ansible-role-virt_install_vm
Have fun!
Ansible Role: virt_install_vm
An Ansible role to install a libvirt virtual machine with virt-install
and cloud-init. It is “designed” to be flexible.
An example template is provided to set up a Debian system.
Requirements
The role is wrapper around the following roles:
- stafwag.qemu_img: https://github.com/stafwag/ansible-role-qemu_img
- stafwag.cloud_localds: https://github.com/stafwag/ansible-role-cloud_localds
- stafwag.virt_install_import: https://github.com/stafwag/ansible-role-virt_install_import
Install the required roles with
$ ansible-galaxy install -r requirements.yml
this will install the latest default branch releases.
Or follow the installation instruction for each role on Ansible Galaxy.
https://galaxy.ansible.com/stafwag
Supported GNU/Linux Distributions
It should work on most GNU/Linux distributions.
cloud-cloudds is required. cloud-clouds was available on
Centos/RedHat 7 but not on Redhat 8. You’ll need to install it manually
to use it role on Centos/RedHat 8.
- Archlinux
- Debian
- Centos 7
- RedHat 7
- Ubuntu
Role Variables and templates
Variables
See the documentation of the roles in the Requirements section.
-
virt_install_vm: “namespace”
-
skip_if_deployed: boolean default: false.
When true: Skip role if the VM is already deployed. The role will exit successfully. When false: The role will exit with an error if the VM is already deployed.
-
Templates.
templates/simple_debian: Example template to create a Debian virtual machine.
This template use cloud_localds.cloudinfo to configure the cloud-init user-data.
See the Usage section for an example.
Usage
Create a virtual machine template
This is a file with the role variables to set set up a virtual machine with all the common settings for the virtual machines.
In this example vm.hostname and vm.ip_address can be configured
for each virtual machine.
- debian_vm_template.yml:
qemu_img:
dest: "/var/lib/libvirt/images/.qcow2"
format: qcow2
src: /Downloads/isos/debian/cloud/debian-10-generic-amd64.qcow2
size: "50G"
owner: root
group: kvm
mode: 660
cloud_localds:
dest: "/var/lib/libvirt/images/_cloudinit.iso"
config_template: "templates/simple_debian/debian.j2"
network_config_template: "templates/simple_debian/debian_netconfig.j2"
cloud_config:
system_info:
default_user:
name: ansible
passwd: ""
ssh_authorized_keys:
- ""
network:
dns_nameservers:
9.9.9.9
dns_search:
intern.local
interface:
name:
enp1s0
address:
""
gateway:
192.168.123.1
disable_cloud_init: true
reboot:
true
virt_install_import:
wait: 0
name: ""
os_type: Linux
os_variant: debian10
network: network:default
graphics: spice
disks:
- "/var/lib/libvirt/images/.qcow2,device=disk"
- "/var/lib/libvirt/images/_cloudinit.iso,device=cdrom"
Playbook
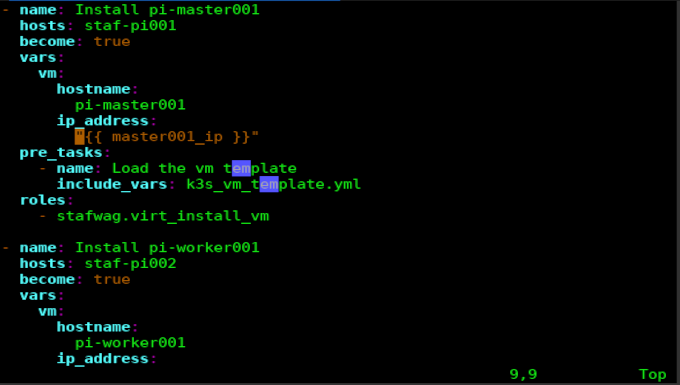
Playbook to setup a virtual machine:
- name: Install tstdebian2
hosts: kvmhost
become: true
vars:
vm:
hostname:
tstdebian2
ip_address:
192.168.123.2/24
pre_tasks:
- name: Load the vm template
include_vars: debian_vm_template.yml
- name: display qemu_img
debug:
msg:
- "qemu_img: "
roles:
- stafwag.virt_install_vm







Leave a comment